Windows Living off the Land
LOLBAS stands for Living Off the Land Binaries And Scripts, a project's primary main goal is to gather and document the Microsoft-signed and built-in tools used as Living Off the Land techniques, including binaries, scripts, and libraries.
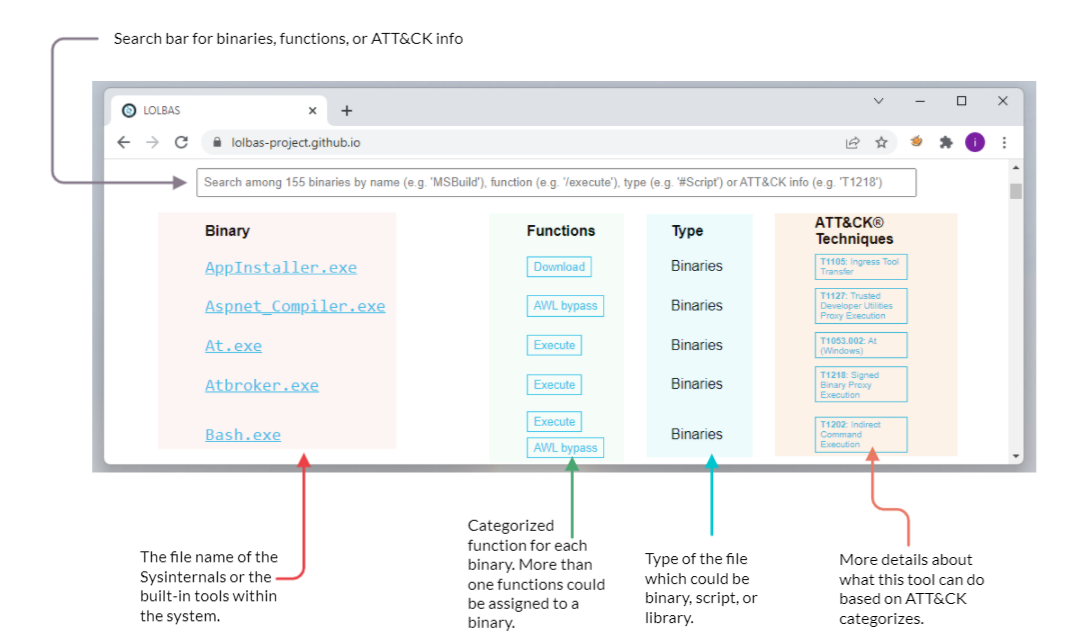
The LOLBAS project is a community-driven repository gathering a collection of binaries, scripts, libraries that could be used for red team purposes. It allows to search based on binaries, functions, scripts, and ATT&CK info. The previous image shows what the LOLBAS project page looks like at this time. If you are interested in more details about the project, you may visit the project's website here.
The LOLBAS website provides a convenient search bar to query all available data. It is straightforward to look for a binary; including the binary name will show the result. However, if we want to look for a specific function, we require providing a / before the function name. For example, if we are looking for all execute functions, we should use /execute. Similarly, in order to look based on types, we should use the # symbol followed by the type name. The following are the types included in the project:
Script
Binary
Libraries
OtherMSBinaries
Interesting Functionalities
The LOLBAS project accepts tool submissions that fit one of the following functionalities:
Arbitrary code execution
File operations, including downloading, uploading, and copying files.
Compiling code
Persistence, including hiding data in Alternate Data Streams (ADS) or executing at logon.
UAC bypass
Dumping process memory
DLL injection
File Operations
Certutil
Certutil is a Windows built-in utility for handling certification services. It is used to dump and display Certification Authority (CA) configuration information and other CA components. Therefore, the tool's normal use is to retrieve certificate information. However, people found that certutil.exe could transfer and encode files unrelated to certification services.
To illustrate this with an example, we can use certutil.exe to download a file from an attacker's web server and store it in the Window's temporary folder, using the command below. Note that we use the-urlcache and -split -f parameters to enforce the tool to download from the provided URL using the split technique.
-urlcache to display URL, enables the URL option to use in the command -split -f to split and force fetching files from the provided URL. Also, the certutil.exe can be used as an encoding tool where we can encode files and decode the content of files. ATT&CK T1027 refers to this technique to obfuscate files to make them difficult to discover or analyze.
BITSAdmin
The bitsadmin tool is a system administrator utility that can be used to create, download or upload Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) jobs and check their progress. BITS is a low-bandwidth and asynchronous method to download and upload files from HTTP webservers and SMB servers. Additional information about the bitsadmin tool can be found at Microsoft Docs
/Transfer to use the transfer option /Download we are specifying transfer using download type /Priority we are setting the priority of the job to be running in the foreground
FindStr
Findstr is a Microsoft built-in tool used to find text and string patterns in files. The findstr tool is useful in that helps users and system administrators to search within files or parsed output. For example, if we want to check whether port 8080 is open on our machine, then we can pipe the result of netstat to find that port as follows: netstat -an| findstr "445".
However, an unintended way was found by using findstr.exe to download remote files from SMB shared folders within the network as follows,
/V to print out the lines that don't contain the string provided.
dummystring the text to be searched for; in this case, we provide a string that must not be found in a file.
> c:\Windows\Temp\test.exe redirect the output to a file on the target machine.
File Execution
This task shows various ways of executing a binary within the operating system. The typical case of executing a binary involves various known methods such as using the command line cmd.exe or from the desktop. However, other ways exist to achieve payload execution by abusing other system binaries, of which one of the reasons is to hide or harden the payload's process. Based on the MITRE ATT&CK framework, this technique is called Signed Binary Proxy Execution or Indirect Command Execution, where the attacker leverages other system tools to spawn malicious payloads. This technique also helps to evade defensive controls.
File Explorer
File Explorer is a file manager and system component for Windows. People found that using the file explorer binary can execute other .exe files. This technique is called Indirect Command Execution, where the explorer.exe tool can be used and abused to launch malicious scripts or executables from a trusted parent process.
The explorer.exe binary is located at:
C:\Windows\explorer.exe for the Windows 64-bit version.
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\explorer.exe for the Windows 32-bit version.
In order to create a child process of explorer.exe parent, we can execute the following command:
WMIC
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMIC) is a Windows command-line utility that manages Windows components. People found that WMIC is also used to execute binaries for evading defensive measures. The MITRE ATT&CK framework refers to this technique as Signed Binary Proxy Execution (T1218)
Rundll32
Rundll32 is a Microsoft built-in tool that loads and runs Dynamic Link Library DLL files within the operating system. A red team can abuse and leverage rundll32.exe to run arbitrary payloads and execute JavaScript and PowerShell scripts. The MITRE ATT&CK framework identifies this as Signed Binary Proxy Execution: Rundll32 and refers to it as T1218.
The rundll32.exe binary is located at:
C:\Windows\System32\rundll32.exe for the Windows 64-bit version.
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\rundll32.exe for the Windows 32-bit version.
Now let's try to execute a calc.exe binary as proof of concept using the rundll32.exe binary:
In the previous command, we used the rundll32.exe binary that embeds a JavaScript component, eval(), to execute the calc.exe binary, a Microsoft calculator.
As we mentioned previously, we can also execute PowerShell scripts using the rundll32.exe. The following command runs a JavaScript that executes a PowerShell script to download from a remote website using rundll32.exe.
As a result of the previous execution, a copy of the script.ps1 downloaded into memory on the target machine.
MSHTA
Mshta is used to run HTA content or an inline script delivered by a document or link.
Application Whitelisting Bypasses
Application Whitelisting is a Microsoft endpoint security feature that prevents malicious and unauthorized programs from executing in real-time. Application whitelisting is rule-based, where it specifies a list of approved applications or executable files that are allowed to be present and executed on an operating system.
Regsvr32
Regsvr32 is a Microsoft command-line tool to register and unregister Dynamic Link Libraries (DLLs) in the Windows Registry. The regsvr.exe binary is located at:
C:\Windows\System32\regsvr32.exe for the Windows 32 bits version
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\regsvr32.exe for the Windows 64 bits version
Besides its intended use, regsvr32.exe binary can also be used to execute arbitrary binaries and bypass the Windows Application Whitelisting. According to Red Canary reports, the regsvr32.exe binary is the third most popular ATT&CK technique. Adversaries leverage regsvr32.exe to execute native code or scripts locally or remotely. The technique used in the regsvr32.exe uses trusted Windows OS components and is executed in memory, which is one of the reasons why this technique is also used to bypass application whitelisting.
Let's try to apply this technique in real life. First, we need to create a malicious DLL file using msvenom and set up our Metasploit listener to receive a reverse shell. Note that we will be creating a malicious file that works for 32bit operating systems. We will be using the regsvr32.exe Application Whitelisting Bypass technique to run a command on a target system.
Note that we specified the output type as DLL using the-f argument. Once the malicious DLL file is generated, we need to deliver the payload to the victim machine. We will do this by using a webserver to serve the DLL file on our attacking machine as follows,
From the victim machine, visit the webserver of the attacking machine on port 1337 that we specify. Note that this port can be changed with your choice!
On the victim machine, once the file DLL file is downloaded, we execute it using regsvr32.exe as follows,
or
With the second option, which is a more advanced command, we instruct the regsvr32.exe to run:
/s: in silent mode (without showing messages)
/n: to not call the DLL register server
/i:: to use another server since we used /n
/u: to run with unregister method
On the attacking machine, we should receive a reverse shell.
Note if we wanted to create a 64-bit DLL version, we need to specify it in the msfvenom command and run it from the victim machine using the 64bits version of regsvr32.exe at C:\Windows\SysWOW64\regsvr32.exe.
BASH
In 2016, Microsoft added support for the Linux environment on Windows 10,11, and Server 2019. This feature is known as Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), and it exists in two WSL versions: WSL1 and WSL2. WSL is a Hyper-V virtualized Linux distribution that runs on the operating system, supporting a subset of the Linux kernel and system calls. This feature is an addon that a user can install and interact with a Linux distribution. As part of WSL, bash.exe is a Microsoft tool for interacting with the Linux environment.
People found ways to execute payloads and bypass the Windows application whitelisting since it is a Microsoft signed binary. By executing bash.exe -c "path-to-payload", we can execute any unsigned payload. ATT&CK called this an Indirect Command execution technique where attackers abuse the Windows tools utility to obtain command executions. For more information about this technique, you may visit the T1202 ATT&CK website.
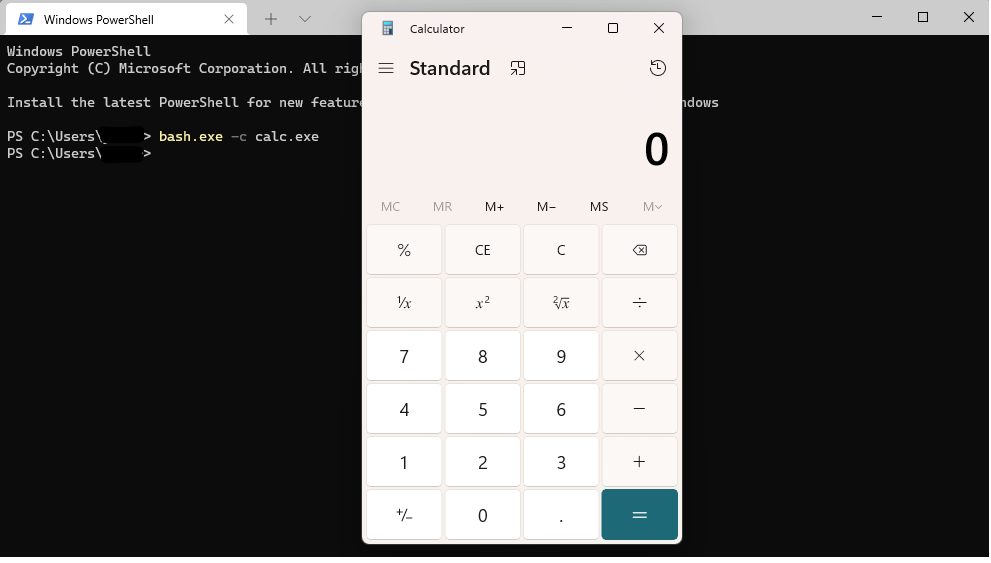
Note that you need to enable and install the Windows Subsystem for Linux in Windows 10 to use the bash.exe binary.
Other Techniques
Shortcuts
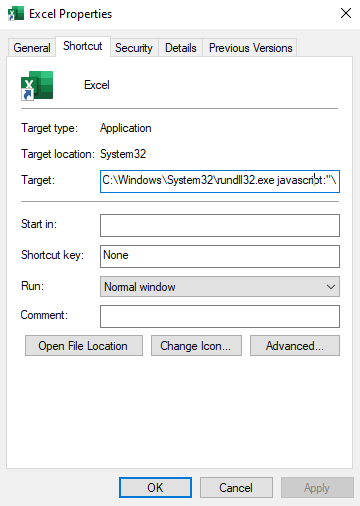
Shortcuts or symbolic links are a technique used for referring to other files or applications within the operating system. Once a user clicks on the shortcut file, the reference file or application is executed. Often, the Red team leverages this technique to gain initial access, privilege escalation, or persistence. The MITRE ATT&CK framework calls this Shortcut modification technique T1547, where an attacker creates or modifies a shortcut in order to take advantage of this technique.
To use the shortcut modification technique, we can set the target section to execute files using:
Rundll32
Powershell
Regsvr32
Executable on disk
The attached figure shows an example of a shortcut modification technique, where the attacker modified the Excel target section to execute a binary using rundll32.exe. We choose to execute a calculator instead of running the Excel application. Once the victim clicks on the Excel shortcut icon, the calc.exe is executed. For more information about shortcut modification, you may check this GitHub repo.
No PowerShell!
In 2019, Red Canary published a threat detection report stating that PowerShell is the most used technique for malicious activities. Therefore, Organizations started to monitor or block powershell.exe from being executed. As a result, adversaries find other ways to run PowerShell code without spawning it.
PowerLessShell is a Python-based tool that generates malicious code to run on a target machine without showing an instance of the PowerShell process. PowerLessShell relies on abusing the Microsoft Build Engine (MSBuild), a platform for building Windows applications, to execute remote code.
First, let's download a copy of the project from the GitHub repo onto the AttackBox:
One of the project requirements is to get a PowerShell payload to make it suitable to work with MSBuild. On the AttackBox, we need to generate a PowerShell payload using msfvenom as follows:
Also, we need to run the Metasploit framework to listen and wait for the reverse shell.
Now that we have the payload ready, change to the PowerLessShell directory project to convert the payload to be compatible with the MSBuild tool. Then run the PowerLessShell tool and set the source file to the one we created with msfvenom as follows:
Once the command is executed successfully, we need to transfer the output file to the Windows machine. You can do this using the SCP command or set a web server to host the file on the AttackBox (python3 -m http.server 1337) and download the file using the browser.
Finally, on the target Windows machine, build the .csproj file and wait for the reverse shell!
Once we run the MSBuild command, wait a couple of seconds till we receive a reverse shell. Note that there will be no powershell.exe process is running.
Last updated